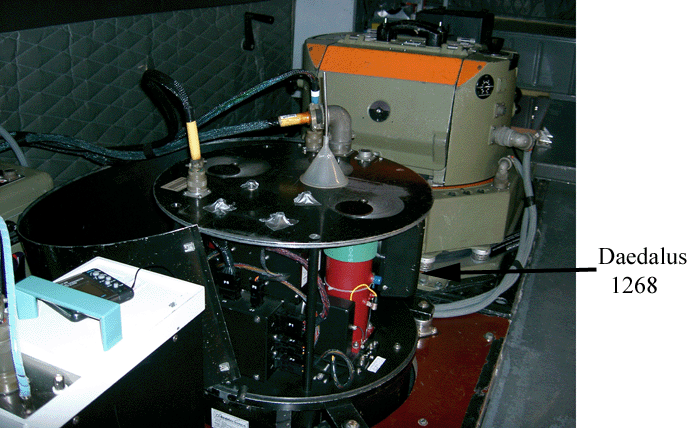
The Daedalus 1268 Airborne Thematic Mapper (ATM) collects radiation from the Earth’s surface in 11 different bandwidths, in the visible, near infrared and thermal bands of the ems. The scanner is a passive remote sensing device, and is designed for use on an airborne platform. It operates by using a rotating scan mirror to capture the radiated light, with both visible and near infrared being split and then imaged onto a number of silicon detectors. The middle infrared and thermal radiation is dealt with slightly differently, as they are split and then recorded onto three single detector elements, which are enclosed within liquid nitrogen cooled containers (see the image below which shows the scanner uncovered).

Bands one to five collect data in the visible part of the spectrum, with bands six to eight in the near infrared, bands nine and ten in the short-wave infrared, and bands eleven and twelve in the same mid infra-red or thermal wavelength, but with channel 12 collected using half the gain setting, thus utilising a different radiometric sensitivity to help alleviate any potential over-exposure problems (only applicable to the data collected in 1992, as updates to the scanner have to a large extent dealt with this problem).